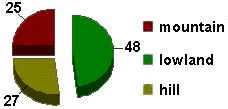Origin of the name:
In the II century before Christ a road was built
in honor of the consul Roman Mark Emilio Facetious that connected Rimini to
Piacenza and it was called Aemilia. From this road the name was given to the
Region. In the VI century after Christ the Romans lost this territory
which was divided between the Longobardis and the Byzantines calling these
lands respectively Longobardia and Romania. The actual zone of Romagna
was of Byzantine dominion. With the unity of Italy, the Region acquired
the aboriginal name of Emilia. Only in 1947 the was the actual name of Emilia
Romagna assigned.
Reliefs - Passes - Coasts -
Islands:
In the southern part of the Region there are the
Appenninichemountains which are not very tall and are formed by friable rocks
that are easily eroded by water which cause frequent landslides and rains
plough through the rock. The line of the Appennino Ligure confines the
Maggioresca Mountain (1799 ms. ). The Appennino Tosco-Emiliano is a faded
mountainous chain, in which a lot of furrows and inlets depart in direction of
the Po. The most important tops are of the Cimone Mountain and the Cusna
Mountains that stretch over a few the 2000 ms. The varied sections of Appennino
take the name of the bordering provincies such as Appennino Piacentino,
Parmense, Reggiano Modenese, Bolognese, Romagnolo. Some passes connect
Emilia Romagna with Tuscany and Liguria. Between those Tuscans we remember the
Footstep of the Cisa, the Footstep Cerretto, the Footstep of the Abetone, the
Footstep of the Futa; the most important footstep that brings in Liguria is
Footstep of One hundred Crosses. The lowland, is formed by the southern part of
the Lowland Padana. From west toward the east the lowland widens more and
more, arriving to the adriatic coast with a great width of the Venetian
lombardo. The earths of this lowland are very fertile.
| Landscape: |
| The conformation of the
Region is divided in two completely different sections from each other: the
first one, situated in the southern part of the Region,is all mountainous and
hilly; the second, the northern one is all level. The mountain is characterized
by a feeling of abandonment and loneliness, putting each other in clear
contrast with the nature that instead introduces other very inhabited parts
rich with a variety of cultivations, and roads full of traffic and as
well as different rivers and channels that irrigate the country. The orchards
are cultivated as far as the eye can see and the fields with old farms adorn
these colored landscapes. Also on the adriatic shore we find two conflicting
aspects: the wild and silent valleys and of the lagoons and the the
beaches overcrowded with lots of tourist structures along the coastal. |

The Towers in the historical center in Bologna
|
Agriculture - Stock-farm -
Fishing:
The agriculture of the Region is amoung the most
advanced of Italy. We find a big variety of products and a abundance of
some of them. This fertility is owed to the favorable geographical and climatic
position and also because modern techniques of cultivation and organization of
commerce are used. The Emilia Romagna prospers in the crops of wheat and
sugar beets; and also the production of rice, bowline, wine and fruit. Only in
this sector of the fruit big cultivations are those of plums, ciliege, apricots
and pears. In the sector vinicolos there are some wines that are very important
such as the Lambrusco, St. Giovese, the Albana. Within the vegetable catagorie
are notable quantities of onions, peas and tomatoes. Also cultivated are hemp
and flax. The most practiced breeding is that of cattle and swines. Emilia
Romagna produces a fifth of the national product of butchered livestock and a
sixth of the milk. The pig meat is used for the production of meats. From the
milk traditional cheeses are produced: nuisance and parmigiano. The breeding of
chickens is also well developed. The most intense zone for fishing is the
Valleys of Comacchio, where they raise over each other and where eels are
fished. The most abundant fish are blue fish.
| Industry - Tourism: |

Mausoleum of Teodorico in Ravenna
|
Characteristic of
emiliano-romagnola, is the lack of big industrial complexes, which is
tied exclusively to the agricultural products and to breeding. The most
important industries are alimentary ones(vinicole, conserviere, cheese,
sugar-refineries and delicatessen factories), besides those of chemists and
mechanics. One of the most memorable is the factory of Maranello of Ferrari.
The chemical industry and the production of petroleum, also draw on
methane in the lowland romagnola. The bulk of the economy of this Region are in
the pharmaceutical clothes and the ceramics sectors. The regional tourism
also represents a very important factor.
|
Thousand of hotel structures, restaurants and places of
every kind, are distributed along the 70 kilometers of inclusive beach between
Ravenna and Catholic. Also of notible interest are the artistic patrimony
of the cities of Emilia and the varied cities of thermal care as Salsomaggiore
or Porretta Terme.
Position and Frontier:
The region is situated between Adriatic Sea, Po and
Appennino. Emilia Romagna confines to north with Veneto and Lombarda, to east
with Adriatic Sea, to south with Marche, Tuscany, the small State of
S.Marino and a brief line of Liguria. To west it borders Liguria,
Lombardy and a for a short distance Piedmont.
Rivers - Lakes:
The rivers are divided in tributary and sub-tributary
of Po and others that flow in the sea directly. Besides the Po, are its
tributaries: Trebbia, Panaro, Parma, Enza, Bucket and Taro. The rivers that
flow in the Adriatic Sea directly are Rhine and Marecchia. The particularity of
these rivers is their torrential character, they rather dry in the summer and
subjects to floods in winter.
Climate:
The climate is characterized by warm and sultry summers
and rigid winters with abundant precipitation and frequent days of fog and
cold. Along the coastal Adriatic the climate is milder; on the mountains
abundant rains and snowfalls are frequentl. Snow falls also in the
lowlands however here the snow immediately vanishes and is loosened by the
wind.
Population:
The populations move from the mountains especially to
the lowland along the zone of the coastal band, without creating big
agglomerations, but distributing each other in balanced way. The only exception
is for Bologna that is over 400 thousand inhabitants, while the other big
cities are revolve between 100 and the 180 thousand inhabitants. To note is the
curious fact that 8 chief towns, excluded Ravenna and Ferrara, rise along the
street Emilia that represents the principal street of the Region. In this
important street for communication, the concentrations of inhabitants never
reach the level that would be considered overcrowed.
Communication:
The principal road axle of the Region is
still the street Emilia. From this street Emilia the biggest cities have
developed of Emilia Romagna parallelly, over the railway and motorway nets.
From these big arteries of communication the varied ramifications depart toward
the bordering Regions. Bologna is the greatest release road where all the
streets of communication meet. There are two airports, one in Bologna (Borgo
Panigale) and the other in Rimini.
Web Site designed by
MediaSoft - © Copyright 1998-1999 - All rights reserved